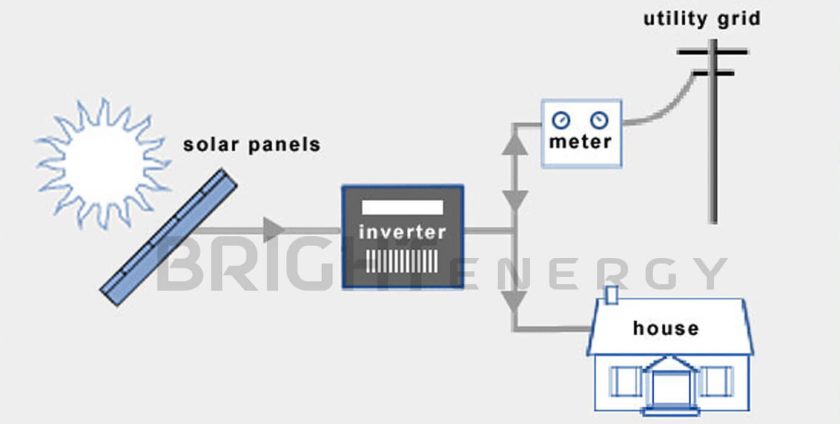
On-grid solar Systems, also known as grid-tied or grid-connected systems, are the more traditional approach to harnessing solar power. These systems are directly connected to the electrical grid, and their operation relies on this connection.
How Does A Grid-Tied Solar System Work?
A grid-tied solar system, also known as a grid-connected or grid-interconnected solar system, is a solar power setup, that is connected to the local electrical grid. Unlike off-grid systems, which operate independently, grid-tied systems are designed to work in conjunction with the existing electrical grid infrastructure.
Components of a Grid-tied Solar System:
Following are the different components of a grid-tied solar system:
Solar Panels:
The system begins with solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, which are installed on the roof or ground-mounted in an area with maximum sunlight exposure. These panels contain solar cells that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity.
There are two different types of solar panels available in the market.
- Monofacial:Charges from one side only
- Bifacial:Charges from both sides
Although monfacial solar panels are cheaper, it is better to install bifacial solar panels as it is the latest technology.
Inverter:
The DC electricity generated by the solar panels is sent to an inverter. The inverter’s primary function is to convert the DC electricity from the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the type of electricity used in homes and businesses.
Electricity Consumption and Net Metering:
Net metering is a billing arrangement for solar energy systems in Pakistan that allows homeowners and businesses to connect their solar panel systems to the electricity grid. The converted AC electricity is used to power your home or business. If the solar system produces more electricity than you need, the excess electricity is sent back to the grid.
Net metering enables you to feed any excess electricity you produce through solar panels back into the grid.
But the question arises how does Net Metering work?
How Does Net Metering Work?
To participate in net metering, you first need to install a solar panel system on your property. These solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity, which you can use to power your home or business.
WAPDA will install a bi-directional (two-way) meter. This special meter is capable of measuring electricity flow in two directions: from the grid to your property and from your solar panels to the grid.
During daylight hours, when your solar panels are generating electricity, any excess electricity that you don’t use immediately is sent back to the WAPDA’s grid through the two-way meter. It is usually 20% to 40% of the energy production. This excess electricity is measured and credited to your account.
At night or when your electricity demand exceeds what your solar panels are producing, you draw electricity from the WAPDA’s grid. The two-way meter keeps track of this as well. Your billing is based on the “net” electricity you consume, which is the difference between what you generate and what you draw from the grid.
If your solar panels generate more electricity than consumption in a given billing period (e.g., a month), the excess electricity is credited to your account. These credits can offset your future electricity bills. In some cases, you may even receive a payment or a reduced electricity bill by WAPDA if you consistently generate surplus electricity.
Grid Connection:
The inverter is connected to your main electrical panel and, consequently, to the grid. It synchronizes the electricity it produces with the grid’s power, ensuring that the electricity is in phase with the grid’s electricity.
Metering and Billing:
A bidirectional meter, also known as a net meter, is installed by the utility company. This meter records both the electricity you consume from the grid and the excess electricity your solar system feeds back into the grid. Your utility provider bills you based on the net difference between the electricity you consume and the electricity your solar system produces and feeds back into the grid. In some regions, you might be credited for the excess electricity at a specific rate.
Grid Stability and Backup:
Grid-tied systems do not usually include energy storage components like batteries. It means when the grid experiences a power outage, your solar system will automatically shut down for safety reasons. It prevents the system from sending electricity back into the grid, which could potentially harm utility workers trying to fix power lines.
However, some advanced grid-tied systems can include backup power solutions to provide electricity to essential loads during an outage.
Benefits of Net Metering:
Some of the benefits of Net Metering are given below.
Cost Savings:
Net metering allows you to offset your electricity costs by selling excess electricity to the grid and receiving credits. It can lead to significant savings on your electricity bills.
Energy Independence:
Net metering provides a degree of energy independence, as you can generate your electricity and rely less on grid electricity, which may be subject to price fluctuations. It is a great way to escape the load shedding of electricity.
Financial Incentives:
In Pakistan, currently, there are zero tariffs and import duties on solar panels if the complete modules and systems are imported. Many neighboring countries have kept their tariffs at 40% which is way more than in Pakistan.
Grid-tied solar systems are popular because they allow homeowners and businesses to save on electricity bills, reduce their carbon footprint, and contribute to a more sustainable energy future while remaining connected to a reliable grid for uninterrupted power supply. Contact Bright Energy for more details about a Grid-Tier Solar System and its suitability to your needs.

Leave a Reply